NetInstall Description
NetInstall is a program that runs on Windows computer that allows you to install MikroTiK RouterOS onto a PC or onto a RouterBoard via an Ethernet network.
You can download Netinstall on our download page.
NetInstall is also used to re-install RouterOS in cases where the the previous install failed, became damaged or access passwords were lost.
- Your device must support booting from ethernet, and there must be a direct ethernet link from the Netinstall computer to the target device. All RouterBOARDs support PXE network booting, it must be either enabled inside RouterOS "routerboard" menu if RouterOS is operable, or in the bootloader settings. For this you will need a serial cable.
Note: For RouterBOARD devices with no serial port, and no RouterOS access, the reset button can also start PXE booting mode. See your RouterBOARD manual PDF for details. For example RB750 PDF
- Netinstall can also directly install RouterOS on a disk (USB/CF/IDE) that is connected to the Netinstall Windows machine. After installation just move the disk to the Router machine and boot from it.
Screenshot
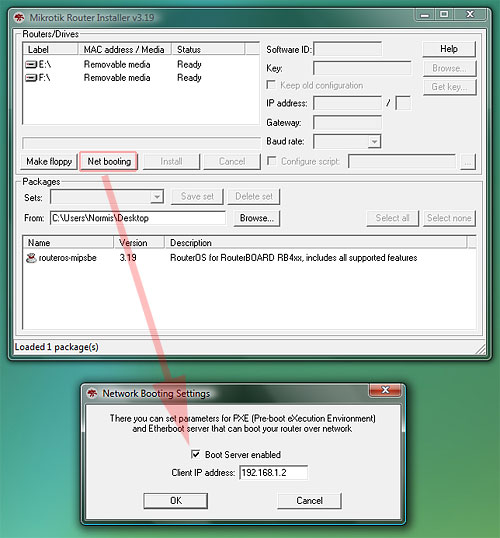
- for installation over network, don't forget to enable the PXE server, and make sure Netinstall is not blocked by your firewall or antivirus. The connection should be directly from your Windows PC to the Router PC (or RouterBOARD), or at least through a switch/hub.
NetInstall Example
This is a step by step example of how to install RouterOS on a RouterBoard 532 from a typical notebook computer.
Requirements
The Notebook computer must be equiped with the following ports and contain the following files:
- Ethernet port.
- Serial port.
- Serial communications program (such as Hyper Terminal)
- The .npk RouterOS file(s) (not .zip file) of the RouterOS version that you wish to install onto the Routerboard.
- The NetInstall program available from the Downloads page at www.mikrotik.com
Connection process
- Connect the routerboard to a switch, a hub or directly to the Notebook computer via Ethernet. The notebook computer Ethernet port will need to be configured with a usable IP address and subnet. For example: 10.1.1.10/24
- Connect the routerboard to the notebook computer via serial, and establish a serial communication session with the RouterBoard. Serial configuration example in in the Serial console manual
- Run the NetInstall program on your notebook computer.
- Press the NetInstall "Net Booting" button, enable the Boot Server, and enter a valid, usable IP address (within the same subnet of the IP address of the Notebook) that the NetInstall program will assign to the RouterBoard to enable communication with the Notebook computer. For example: 10.1.1.5/24
- Set the RouterBoard BIOS to boot from the Ethernet interface.
Configuring Bootloader
To access Routerboard BIOS configuration: reboot the Routerboard while observing the activity on the Serial Console. You will see the following prompt on the Serial Console “Press any key within 2 seconds to enter setup” indicating that you have a 1 or 2 second window of time when pressing any key will give you access to Routerboard BIOS configuration options.
(press any key when prompted):
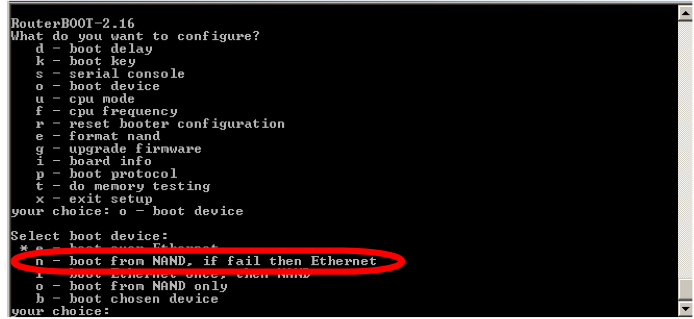
You will see the following list of available BIOS Configuration commands. To set up the boot device, press the 'o' key:
What do you want to configure? d - boot delay k - boot key s - serial console l - debug level o - boot device b - beep on boot v - vga to serial t - ata translation p - memory settings m - memory test u - cpu mode f - pci back-off r - reset configuration g - bios upgrade through serial port c - bios license information x - exit setup
Next Selection: Press the 'e' key to make the RouterBoard to boot from Ethernet interface:
Select boot device: * i - IDE e - Etherboot 1 - Etherboot (timeout 15s), IDE 2 - Etherboot (timeout 1m), IDE 3 - Etherboot (timeout 5m), IDE 4 - Etherboot (timeout 30m), IDE 5 - IDE, try Etherboot first on next boot (15s) 6 - IDE, try Etherboot first on next boot (1m) 7 - IDE, try Etherboot first on next boot (5m) 8 - IDE, try Etherboot first on next boot (30m)
The RouterBoard BIOS will return to the first menu. Press the 'x' key to exit from BIOS. The router will reboot.
Installation
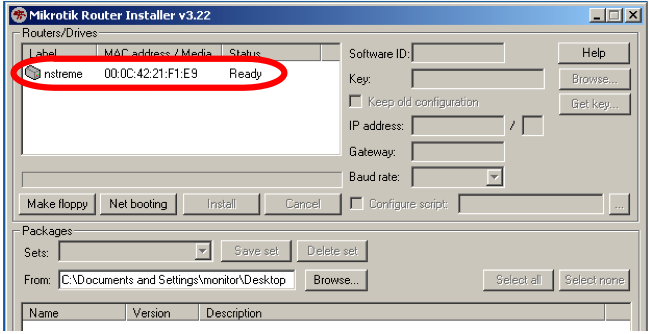
Watch the serial console as the RouterBoard reboots, it will indicate that the RouterBoard is attempting to boot to the NetInstall program. The NetInstall program will give the RouterBoard the IP address you entered at Step 4 (above), and the RouterBoard will be ready for software installation. Now you should see the MAC Address of the RouterBoard appear in the Routers/Drives list of the NetInstall program.
Click on the desired Router/Drive entry and you will be able to configure various installation parameters associated with that Router/Drive entry.
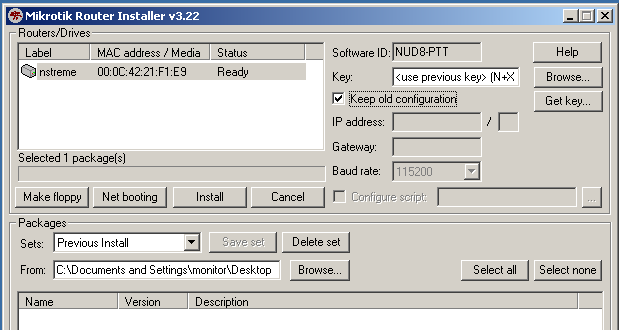
For most Re-Installations of RouterOS on RouterBoards you will only need to set the following parameter:
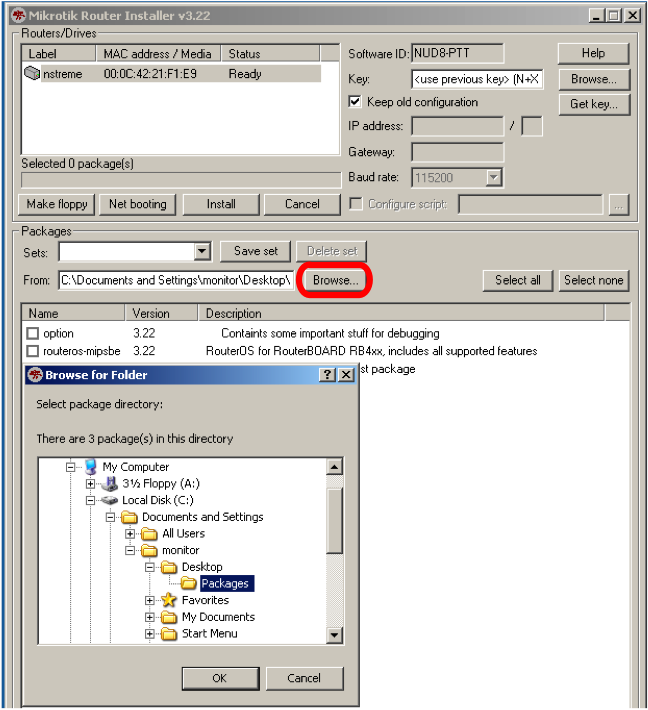
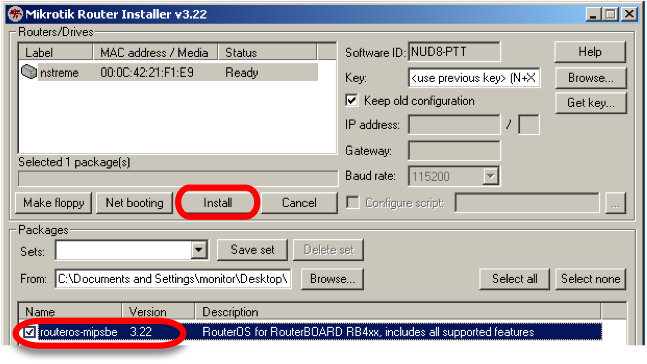
Press the "Browse" button on the NetInstall program screen. Browse to the folder containing the .npk RouterOS file(s) of the RouterOS version that you wish to install onto the Routerboard.
When you have finalized the installation parameters, press the "Install" button to install RouterOS.
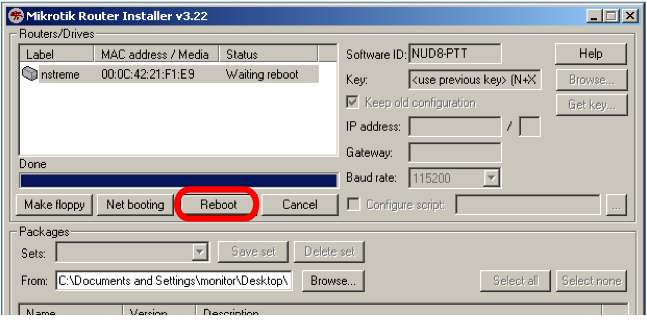
When the installation process has finished, press 'Enter' on the console or 'Reboot' button in the NetInstall program.
Cleanup
1. Reset the BIOS Configuration of the RouterBoard to boot from its own memory.
2. Reboot the RouterBoard.
Reset RouterOS Password
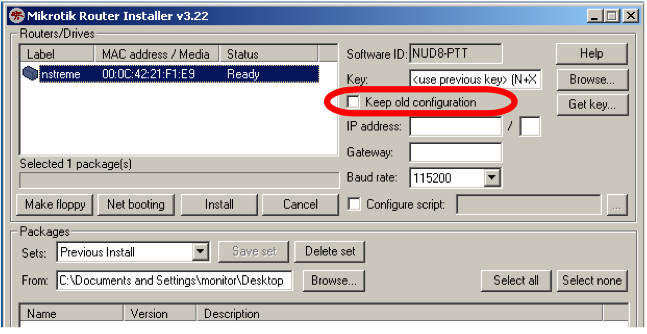
Netinstall can be used to reset password of RouterOS by erasing all configuration from the router. Uncheck 'Keep Old Configuration' during Netinstall and proceed with standard procedure,